AI’s advantages in healthcare

Artificial intelligence is being applied to the healthcare industry in a variety of ways, including generating new medications, helping with procedures, and responding to patient inquiries.
How might healthcare benefit from artificial intelligence?
The artificial intelligence (AI) healthcare market is expected to grow from its estimated $11 billion value in 2021 to $187 billion by 2030, according to Statista. Given that significant growth, the ways in which hospitals, pharmaceutical and biotechnology companies, medical providers, and other players in the healthcare sector operate are probably going to continue to change significantly.
AI is being used more and more in the healthcare sector, and this is speeding development at a faster rate thanks to factors like cheaper hardware, better access to data, improved machine learning (ML) algorithms, and the arrival of 5G. Large amounts of health data, including genetic data, clinical study results, and medical records, may be sorted through and analyzed far more quickly by AI and ML systems than by humans.
AI might improve healthcare. AI has the potential to improve operational efficiency in the healthcare industry.
AI is being used by healthcare organizations to increase the effectiveness of a variety of activities, including patient care and back-office work. Here are a few instances of how AI might help both staff and patients:
- Administrative workflow: Completing paperwork and other administrative duties takes a lot of time for healthcare professionals. Many of those repetitive chores can be completed with the aid of AI and automation, freeing up employee time for other pursuits and increasing their in-person interactions with patients. Generative AI, for instance, can assist medical professionals in taking notes and summarizing content to ensure that medical records are as comprehensive as possible. Accurate coding, information exchange between departments, and billing are further areas where AI may be helpful.
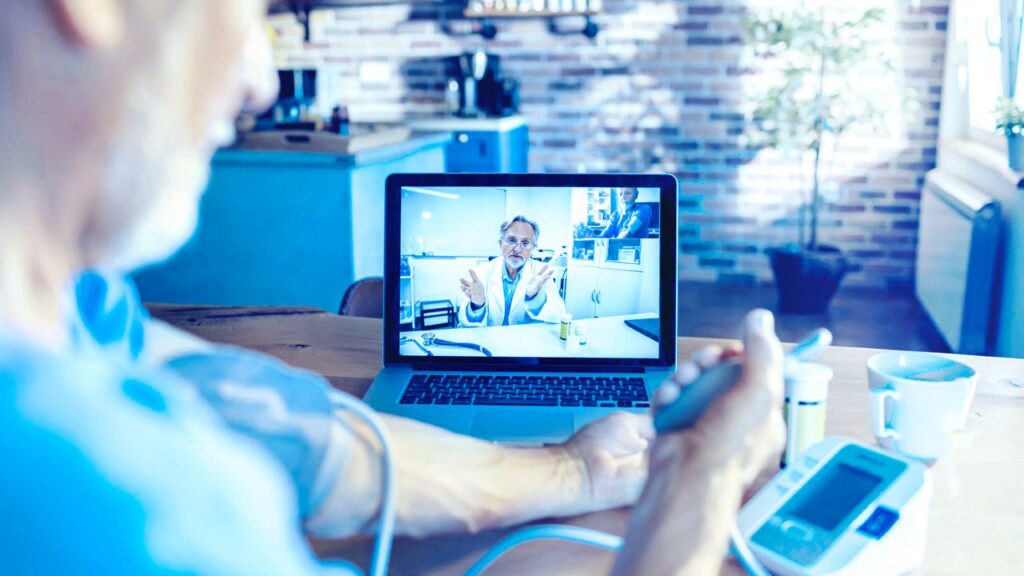
- Virtual nursing assistants: According to a survey, 64% of patients feel at ease using artificial intelligence (AI) to get responses from support nurses around-the-clock. AI virtual nursing assistants, or chatbots, apps, or other interfaces driven by AI, can aid with drug inquiries, report cases to physicians or surgeons, and help patients make an appointment with a doctor. Routine tasks like these can relieve clinical staff members of some of their workload so they can focus more of their time on patient care, which is mostly a human interaction and judgment call.
- Reduced dosage errors: Artificial Intelligence (AI) may be used to find mistakes made by patients when self-administering medicine. One such study that was published in Nature Medicine revealed that up to 70% of individuals do not take insulin as directed. Errors in the patient’s administration of an insulin pen or inhaler could be detected by an AI-powered device that operates in the background (much like a Wi-Fi network).
- Less invasive surgeries: To help lower blood loss, infection risk, and post-surgery pain, AI-enabled robots may be utilized to operate around delicate organs and tissues.