Unraveling the Marvels of Bioprinting in Healthcare
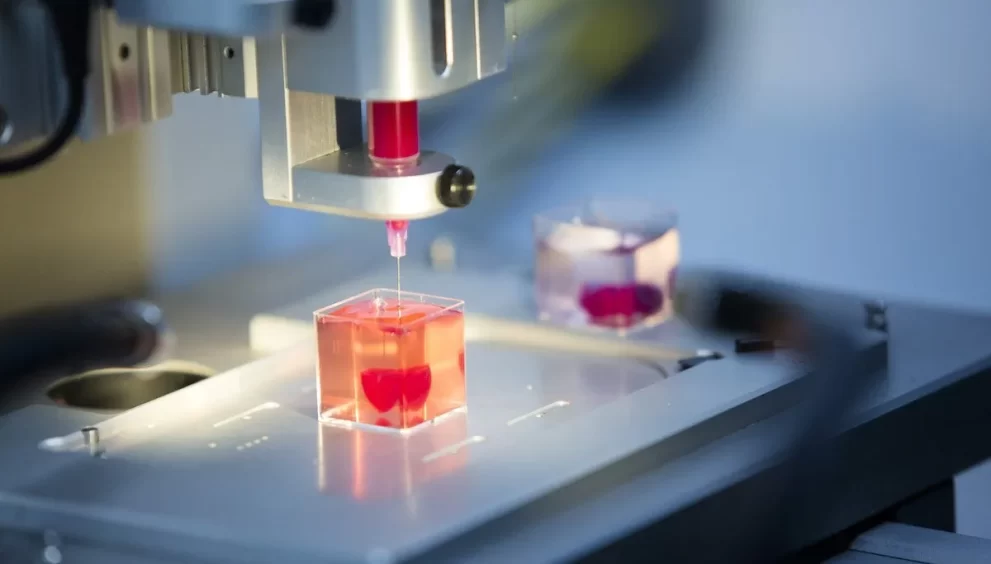
In the landscape of modern healthcare, bioprinting emerges as a remarkable technological innovation with profound implications. This cutting-edge technique, often likened to 3D printing for tissues and organs, holds immense promise for transforming medical treatments and procedures. By harnessing the power of living cells, biomaterials, and sophisticated printing technology, bioprinting offers unprecedented opportunities for regenerative medicine, personalized treatments, and advancements in biomedical research. Let us embark on a journey to explore the wonders of bioprinting and its potential to revolutionize healthcare as we know it.
Advancements in Bioprinting Technology:
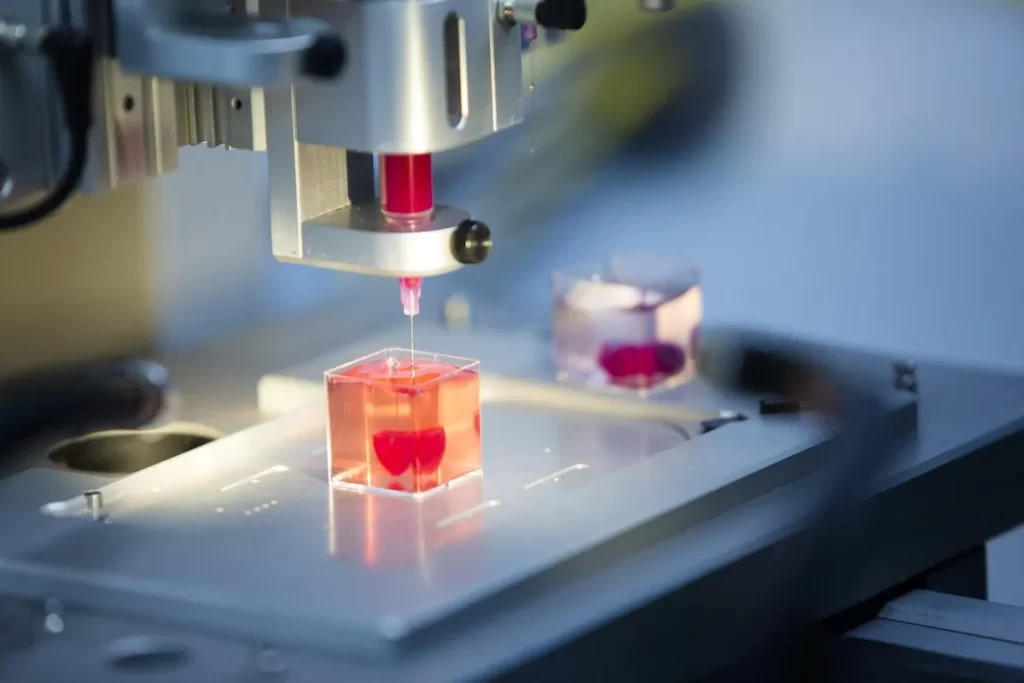
Bioprinting technology has evolved rapidly in recent years, driven by advancements in materials science, cell biology, and engineering. Today, state-of-the-art bioprinters are capable of precisely depositing multiple cell types, biomaterials, and bioactive molecules to create intricate tissue structures with remarkable accuracy and fidelity. These bioprinted tissues can closely mimic the complexity and functionality of native tissues and organs, offering new possibilities for regenerating damaged or diseased tissues and organs.
Applications in Regenerative Medicine:
One of the most promising applications of bioprinting is in regenerative medicine, where the technology holds the potential to revolutionize the treatment of injuries, diseases, and congenital defects. Bioprinted tissues and organs can serve as substitutes for damaged or dysfunctional tissues, providing patients with personalized grafts that are compatible with their own biology. From skin grafts for burn victims to complex organs such as kidneys and hearts, bioprinting offers a pathway to address the growing demand for organ transplantation and tissue replacement therapies.
Personalized Medicine and Drug Discovery:
Bioprinting also holds promise for advancing personalized medicine and drug discovery efforts. By creating patient-specific tissue models using bioprinting technology, researchers can replicate the unique characteristics of an individual’s physiology and disease pathology. These 3D tissue models can be used to study disease mechanisms, screen potential drug candidates, and evaluate treatment responses in a controlled laboratory setting. Additionally, bioprinted tissues can help reduce reliance on animal models in preclinical research, leading to more accurate predictions of drug efficacy and toxicity in humans.
Challenges and Future Directions:
Despite its considerable promise, bioprinting still faces several challenges that must be addressed to realize its full potential in healthcare. These include issues related to scalability, vascularization, immune compatibility, and regulatory approval. Overcoming these challenges will require continued investment in research and development, interdisciplinary collaboration, and regulatory support to ensure the safe and effective translation of bioprinting technologies from the laboratory to the clinic. Additionally, ongoing advancements in materials science, bioengineering, and biotechnology are poised to further enhance the capabilities of bioprinting and expand its applications in healthcare. Bioprinting represents a paradigm shift in healthcare, offering new avenues for regenerative medicine, personalized treatments, and biomedical research. By harnessing the power of living cells and advanced printing technology, bioprinting has the potential to revolutionize the way we diagnose, treat, and prevent disease. As researchers continue to push the boundaries of what is possible, the future of bioprinting holds immense promise for improving patient outcomes, advancing scientific knowledge, and shaping the future of healthcare.